Create a Camera
In order to define an application, the configuration of a camera is necessary, as it provides the video stream.
Cameras
Video streams can be obtained directly from cameras using standard transmission protocols. The diagram below illustrates the connection of a camera via RTSP as an example.
Camera Overview
The camera overview (URL path: /isarsoft/app/cameras) displays all cameras installed in the system, either with thumbnails or in a list. Cameras can be added, edited, or deleted from this overview. Deleting a camera also deletes all applications accessing it and their data. Finding cameras is made easy through a filter and search function.
Configuration
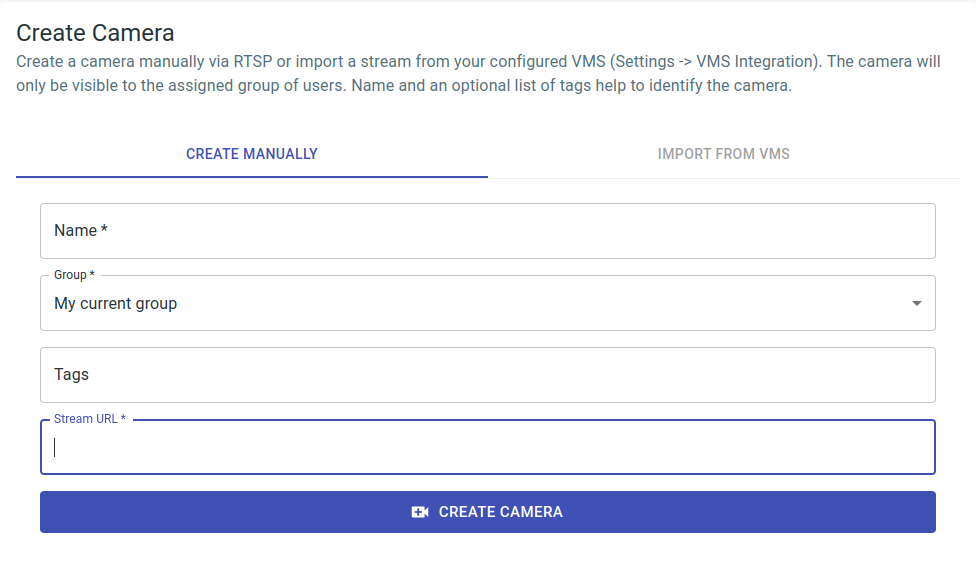
A camera is configured via cameras > camera overview > create camera, or it can be reached via the URL path /isarsoft/app/cameras/add.
Cameras can either be created manually via stream URL or imported from the VMS. Cameras are only visible to users within the specified group. The camera name, along with an optional list of tags, facilitates easy identification.
The stream URL depends on the camera manufacturer. As an example, it may appear like this for an Axis camera: rtsp://[username]:[password]@[ip]:[port]/axis-media/media.amp.
Once the camera is created, additional information, such as location and georeferencing, can be optionally stored for the camera.
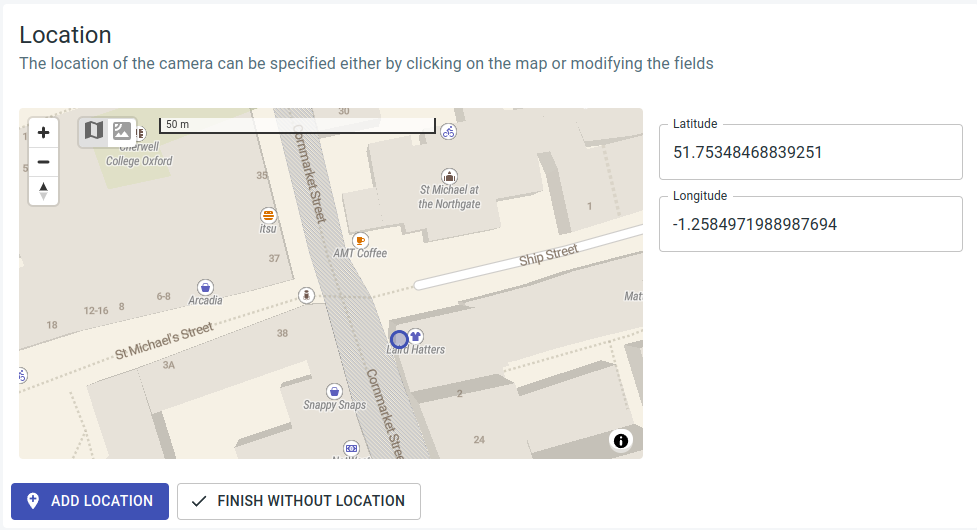
Location
The interactive configuration of the location uses a map for which an internet connection is necessary for loading map data. The position can be refined using GPS coordinates in the latitude and longitude fields.
Storing the location is solely for the sake of clarity and completeness in the configuration and does not impact georeferencing.
Georeferencing
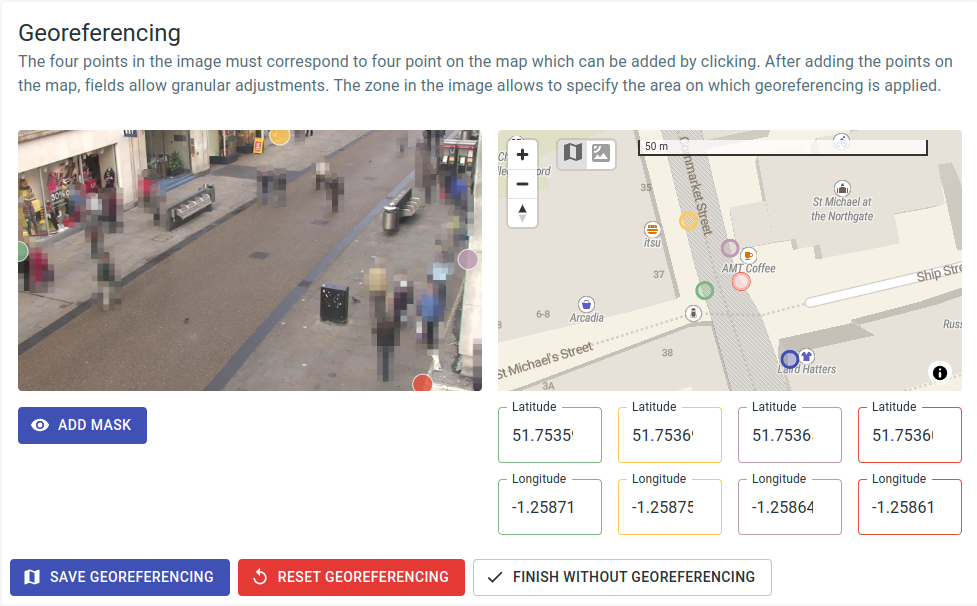
If georeferencing information is saved in the camera, applications like Object Flow can ascertain the position of objects, such as people and vehicles, in GPS coordinates and calculate derived values like speed in meters per second. The blue point in the image at the bottom right represents the camera's position and is not adjustable here.
To incorporate georeferencing, aligning four points (green, yellow, purple, and red) in the image with corresponding points of the same color on the map is necessary. An internet connection is essential to load map data. The points on the map can be refined using the latitude and longitude fields marked in the respective color.
To ensure proper functioning of georeferencing, it is essential that all points lie on a flat plane. For optimal results, the area covered by the 4 points (green, yellow, purple, and red) should be as extensive as possible. Placing more than 2 points on a line or having 2 points in the same location is not permitted.
Georeferencing can be restricted to a specific image area by defining a mask. This is particularly important when objects in the image exhibit movement not only in a single plane but with a height shift to that plane, such as when navigating stairs. Georeferencing is always conducted with the assumption that objects move on the configured plane (the "floor"). Height shifts in areas not excluded by the mask can introduce errors in the collected motion profiles. Additionally, if the camera is angled very flat (parallel to the plane) and objects are positioned at a considerable distance, resulting in their reduced size, it may also be beneficial to restrict georeferencing.
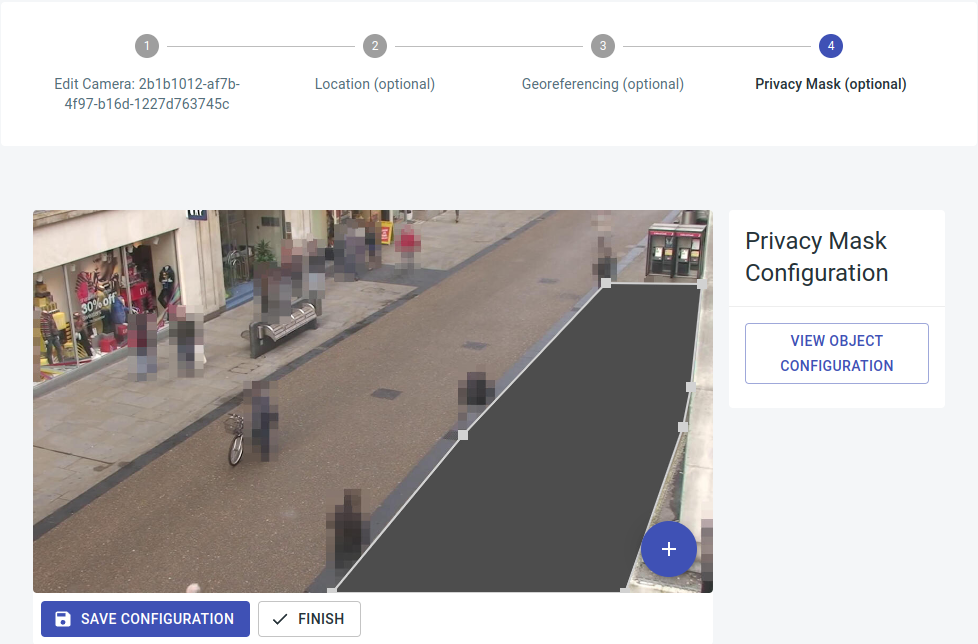
Privacy masks
Privacy masks are customizable regions that can be obscured in the software. Once configured, no further evaluations occur within these designated areas.
To add privacy masks, navigate to the "Cameras" section, select the desired camera, and access "Edit settings." You can then directly call and edit Option 4, "Privacy Mask (optional)." It is possible to insert any number of privacy masks.
Background change
Cameras provide the capability to detect changes in the background. This involves comparing running averages from the previous day with the current image. Users can be notified about background changes and respond accordingly through a threshold-based alarm system.